
为推动数学、统计学与其他学科的交叉研究,促进复杂系统相关研究领域专家学者之间的学术交流,为我校师生搭建交流平台,广东外语外贸大学数学与统计学院将于2019年6月21日(周五)下午在大学城校区举办“第一届复杂系统前沿问题学术研讨会”。会议将邀请国内外数学、统计学等领域专家作学术报告,并开展学术讨论。
一、会议邀请报告人
庾建设 教 授(广州大学) 周天寿 教 授(中山大学)
邹 为 副教授(华南师范大学) 张家军 副教授(中山大学)
曾才斌 副教授(华南理工大学) 王浩华 副教授(海南大学)
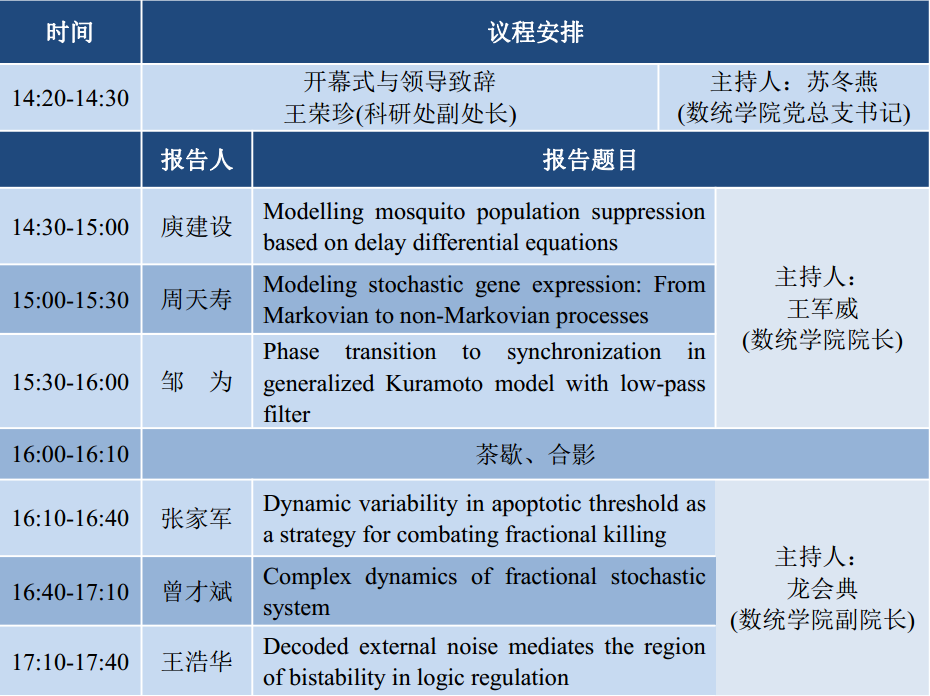
二、会议日程
时间:2019年6月21日(周五)14:20-17:40
地点:广外大学城校区院系楼152会议室
三、报告摘要及主讲人介绍
报告一:Modelling mosquito population suppression based on delay differential equations 庾建设(广州大学教授)
报告摘要:Mosquito-borne diseases are threatening half of the world’s population. A novel strategy of disease control is to suppress the mosquito population by releasing male mosquitoes infected by a special strain of Wolbachia. This bacterium induces cytoplasmic incompatibility that eggs of wild females mated with released males fail to hatch. In this work, we introduce a model of delay differential equations to initiate a study on the mosquito suppression dynamics with the compensation policy that the loss of released males is compensated by new releasing, and the constant policy that a constant amount c of infected males are released each time, T days apart. We find the exact value of the threshold releasing intensity r∗for the compensation policy, and provide a reasonably sharp estimate of the threshold constant c∗for the constant policy. In the first case, we also show that the model displays bi-stability with two stable steady-states and one unstable steady-state when the abundance of released males R(t) 2 (0; r∗). Our simulation reveals that some solutions may develop sustained oscillations with increasing magnitudes, and suggest the existence of one or more stable periodic solutions. The simulation provides a theoretical support to the observation in the Guangzhou mosquito control program that a 5:1 releasing ratio between the releasing amount and the initial wild male abundance could be an optimal option. It also indicates that the suppression efficacy is insensitive to the waiting days between two consecutive releases.
主讲人介绍:庾建设,教授,博士生导师,原广州大学校长,国家杰出青年基金获得者,国家有突出贡献的中青年专家,国家“百千万人才工程”第一层次、第二层次人选,教育部跨世纪优秀人才,现任教育部数学专业教学指导委员会副主任。主要从事微分方程动力系统、差分方程、泛函微分方程及生物数学模型的理论与应用研究,在《J. Differential Equations》、 《SIAM Journal of Applied Mathematics》、《Journal of Mathematical Biology》、《中国科学》等国内外学术期刊发表论文100多篇。先后主持国家自然科学基金项目8项,其中重点项目2项,数学交叉研究平台项目2项;曾获国家级教学成果一等奖1项。
报告二:Modelingstochastic gene expression: From Markovian to non-Markovian processes 周天寿(中山大学教授)
报告摘要:Gene expression is a biochemical process, which may be Markovian but also may be non-Markovian. Modeling and analysis of stochastic gene expression is important for understanding fundamental intracellular processes. This talk will simply introduce how Markovian or non-Markovian processes of stochastic gene expression are modeled and analyzed.
主讲人介绍:周天寿,中山大学数学学院教授,博士生导师,数学研究所所长。主要从事系统生物学和计算生物学研究。在SCI刊物发表一百余篇论文。主持国家基金委重点项目和重大研究计划集成项目。2008年获得国家自然科学二等奖。目前是5个国际学术刊物的编委。
报告三:Phase transition to synchronization in generalized Kuramoto model with low-pass filter 邹为(华南师范大学副教授)
报告摘要:A second-order continuous synchronization has been well documented for the classic Kuramoto model.In this work, we generalize the classic Kuramoto model by incorporating a low-pass filter (LPF) in the coupling, which serves as a simple but novel form of indirect coupling through a common external dynamic environment. We uncover that a first-order explosive synchronization turns out to be a very generic phenomenon in this generalized Kuramoto model with LPF. We establish theoretical results by providing a rigorous analytical treatment, which is validated by conducting extensive numerical simulations. Our study provides a new root for the emergence of first-order explosive synchronization, which could substantially deepen the understanding of the underlying mechanism of a first-order phase transition towards synchronization in coupled dynamical networks.
主讲人介绍:邹为,华南师范大学数学科学学院副教授,广东省青年珠江学者,2010年获得中科院武汉物理与数学研究所应用数学博士学位,博士论文获2011年度中国科学院百篇优秀博士论文奖,2011年10月至2013年9月获洪堡奖学金在德国柏林洪堡大学从事博士后研究工作,2016年2月至2018年1月在香港浸会大学从事香江学者博士后研究工作,长期从事复杂系统、非线性科学理论研究,在耦合非线性系统群体动力学行为研究问题上取得系列成果。目前已在非线性动力学主流期刊发表SCI论文36篇,其中第一作者论文22篇,包括1篇Nature Communications、1篇Physical Review Letters及11篇Physical Review E。主持并完成国家自然科学基金2项。
报告四:Dynamic variability in apoptotic threshold as a strategy for combating fractional killing 张家军(中山大学副教授)
报告摘要:Fractional killing, which is a significant impediment to successful chemotherapy, is observed even in a population of genetically identical cancer cells exposed to apoptosis-inducing agents. This phenomenon arises not from genetic mutation but from cell-to-cell variation in the activation timing and level of the proteins that regulate apoptosis. To understand the mechanism behind the phenomenon, we formulate complex fractional killing processes as a first-passage time (FPT) problem with a stochastically fluctuating boundary. Analytical calculations are performed for the FPT distribution in a toy model of stochastic p53 gene expression, where the cancer cell is killed only when the p53 expression level crosses an activity apoptotic threshold. Counterintuitively, we find that threshold fluctuations can effectively enhance cellular killing by significantly decreasing the mean time that the p53 protein reaches the threshold level for the first time. Moreover, faster fluctuations lead to the killing of more cells. These qualitative results imply that dynamic variability in threshold is an unneglectable stochastic source, and can be taken as a strategy for combating fractional killing of cancer cells.
主讲人介绍:张家军,副教授,博士生导师。主要从事数学与生命科学的交叉、计算系统生物学相关的研究工作,迄今已经发表国际期刊论文30多篇。主持多项科研项目,包括国家自然科学基金面上项目、国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目、广州市珠江科技新星专项项目、高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金新教师类、中国博士后科学基金特别资助项目、广东省博士启动基金项目、中国博士后科学基金面上资助项目,参与多项国家自然科学重点项目和面上项目等。现任中国工业与应用数学学会数学生命科学专业委员会副秘书长、中国细胞生物学学会功能基因组信息学与系统生物学分会理事、广东省工业与应用数学学会理事、广东省计算数学学会理事、广东省高性能计算学会理事。
报告五:Complexdynamics offractionalstochasticsystem 曾才斌(华南理工大学副教授)
报告摘要:Fractional Brownian motion is a centered self-similar Gaussianprocess with stationaryincrements,which depends on the so-called Hurstparameter. This talk will start by the fine properties of fractional Brownian motion, and then we will present our results on stochastic stability, stochastic bifurcation,and invariant measures of stochastic systems driven by fractional Brownian motion.
主讲人介绍:曾才斌,华南理工大学副教授。研究方向为随机动力系统的理论与应用,分数微积分,随机建模与分析,以及数学与其他学科的交叉研究。主持国家自然科学基金青年项目与面上项目各1项,发表SCI收录学术论文近三十篇。
报告六:Decoded external noise mediates the region ofbistability in logic regulation 王浩华(海南大学副教授)
报告摘要:Gene expression is essentially stochastic and integrates the internal noise and external noise to achieve the biologicalfunction. However, how the external noise affects the phenotype diversity remains elusive. Here, we refine a mechanic model based on experiments in murine embryonic stem cells and analyze the influence of external noise on the region of bistability. By noise decomposition based on the different time scale, we find the external noise can mediate the region of bistability, depending on the manner of logic regulation. Furthermore,there is no bistable state in “AND” logic modulation while there will be bistability in “OR” logic modulation; the external noise will suppress bistability and the internal noise will induce bistability. Moreover, the external amplitude modulation (AM) signal suppress the bistable region is better than frequency modulation (FM) signal, that is, decoded AM signal for cell is priority over the FM signal.
主讲人介绍:王浩华,副教授,博士,毕业于中山大学统计学专业,主要研究方向为系统生物学。以第一作者或通讯作者在国际著名期刊FEBS Letters,Phys. Rev. E,Sci. Rep., Chaos, Molecular Biosys.,等上发表相关文章30余篇,主持国家自然科学基金一项,作为主要参与人参与国家自然科学基金三项,海南省自然科学基金二项,其它项目十余项。此外,作为海南大学数学建模负责人和指导教师,于2011年荣获“全国大学生数学建模优秀指导教师”荣誉称号。
